An Eco-friendly Material – Bamboo
Published on 27 January 2023
Tall, straight, evergreen bamboo is full of vitality and has a wide range of applications, providing us with food, clothing, housing, transportation, tools, cultural arts, and so forth.
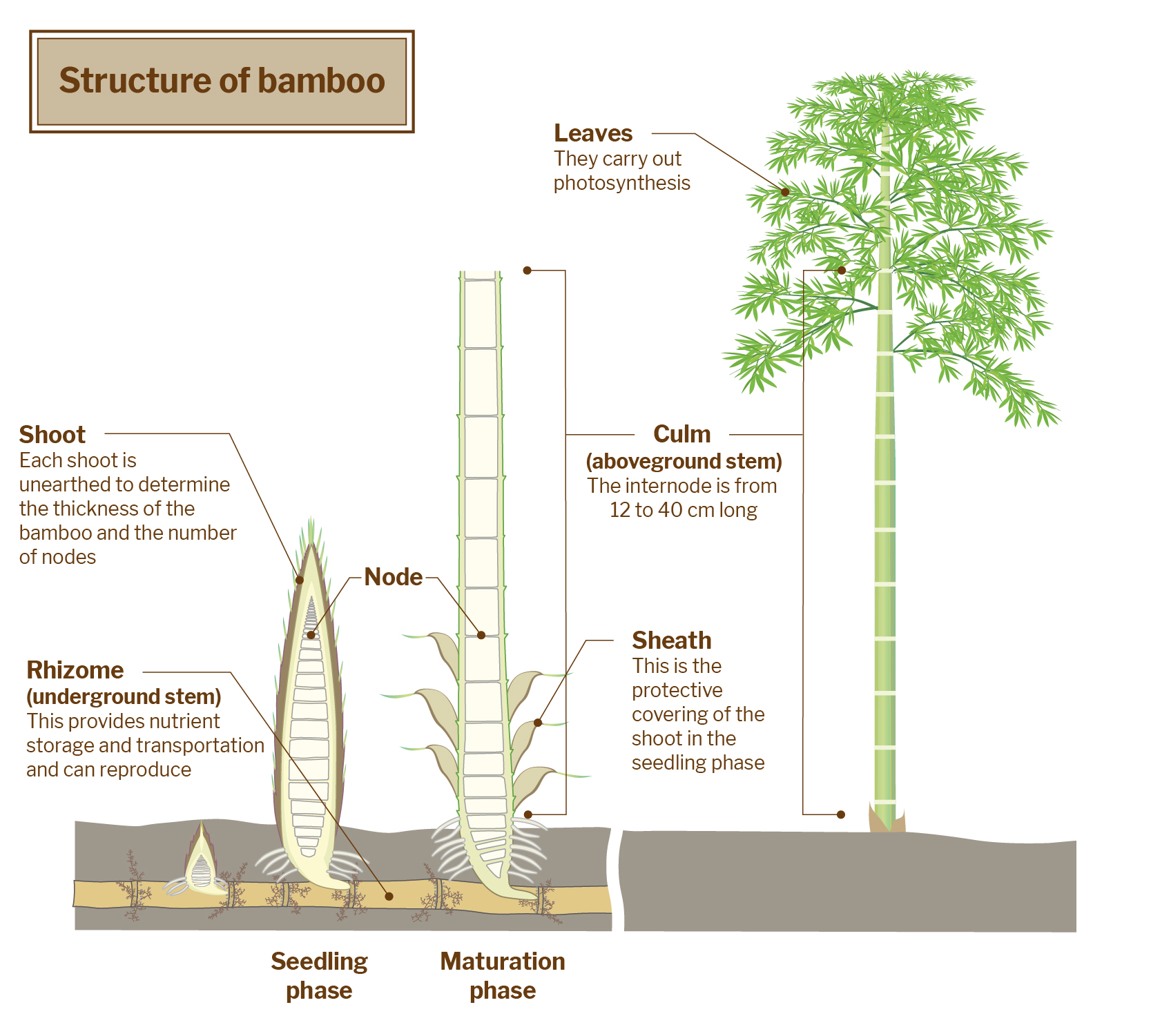
Bamboo is monocotyledonous and belongs to the Poaceae grass family. It is considered to be one of the most primitive grasses. Its main features are bamboo nodes and hollow internodes. Most bamboo is distributed in tropical and subtropical to mild temperate regions, such as East and Southeast Asia and on islands in the Indian and Pacific oceans.
Bamboo is one of the fastest-growing plants in the world, with the maximum growth rate up to 91 cm per day, according to the Guinness World Records, because of intercalary meristems at the nodes of the bamboo culm, which allow rapid stem elongation. Therefore, while other plants only have apical meristems for primary growth, bamboo can grow at every node at the same time. Bamboo usually grows to its full height in a single growing season of three to four months.
Unlike ordinary trees, bamboo culms do not have a vascular cambium and do not exhibit secondary growth through the production of annual rings. In other words, they cannot increase in girth by adding lateral layers of cells. The maximum diameter of the bamboo culm is predetermined as early as the sprouting period. The maximum diameter of various bamboo species varies, with the thickest bamboo culm reaching 30 cm in diameter.
Roots, culms, branches, leaves, shoots, sheaths and other parts of bamboo can be fully utilised. Culms have the most diverse use because of their excellent characteristics, such as high strength, good elasticity and stable performance, making them suitable for construction materials, furniture, weaving, handicrafts, paper making, daily necessities, utensils, and so forth. Today, bamboo is identified as a green and sustainable material because of its short growth cycle, fast growth, wide distribution range and abundant yields.